Alternative payment methods: offer customers more ways to pay
Embracing Alternative Payment Methods (APMs) is imperative in today's fiercely competitive digital commerce landscape. Our research finds 69% of UK consumers abandon their carts when their preferred payment method is unavailable. Quiz consumers in any other market, and you'll likely find similar results, underscoring the importance of merchants understanding their customers' payment preferences and offering a diverse range of payment options at the checkout.
In this blog, we'll explore alternative payment methods by looking at the following:
What are alternative payment methods?
The growth of APMs around the world
The benefits of APMs to merchants and their customers
The different types of alternative payment methods.
What are alternative payment methods?
An Alternative Payment Method (APM) encompasses any payment method that isn't cash or a debit and credit card affiliated with a major international scheme.
APMs can have global reach; examples include Paypal, Apple Pay and Google Pay, and Klarna. Or they can be highly localized. EPS, for example, is an Austrian payment method accepted by 80% of online retailers in the country. While in Belgium, there is a local card scheme, Bancontact, which is anything but an alternative.
The rise of alternative payment methods gives individuals more choice and flexibility in managing their finances. For merchants, the proliferation of APMs has added a layer of complexity to the payment ecosystem. But forward-thinking merchants recognize the opportunity to offer alternative payment methods to meet customer expectations, boost conversion rates, and extend their lifetime value.
Types of alternative payment methods
Account to Account (A2A) payments
The advent of digital banking has spurred the popularity of bank-to-bank payments in the retail sector, making it the fourth most favored payment method worldwide. Bank transfers allow consumers to pay online using direct transfers from their bank account. To complete a bank transfer, customers select the payment method at checkout and then get redirected to their bank to authenticate and authorize the payment.
The rise in open banking technology has enabled more bank transfers, making it incredibly convenient for online retailers and their customers. The extent of the impact and rollout varies depending on the country. In Singapore, more than 65% of the population uses PayNow for one-off and recurring payments.
Buy now, pay later (BNPL)
Buy now, pay later (BNPL) lets customers split purchases into manageable installments with minimal or no interest fees. This payment option appeals to customers looking to make substantial purchases without immediate access to funds. Prominent BNPL providers, such as Klarna, Atome, and Clearpay, have gained popularity in offering this convenient payment solution.

Cash-based electronic payments
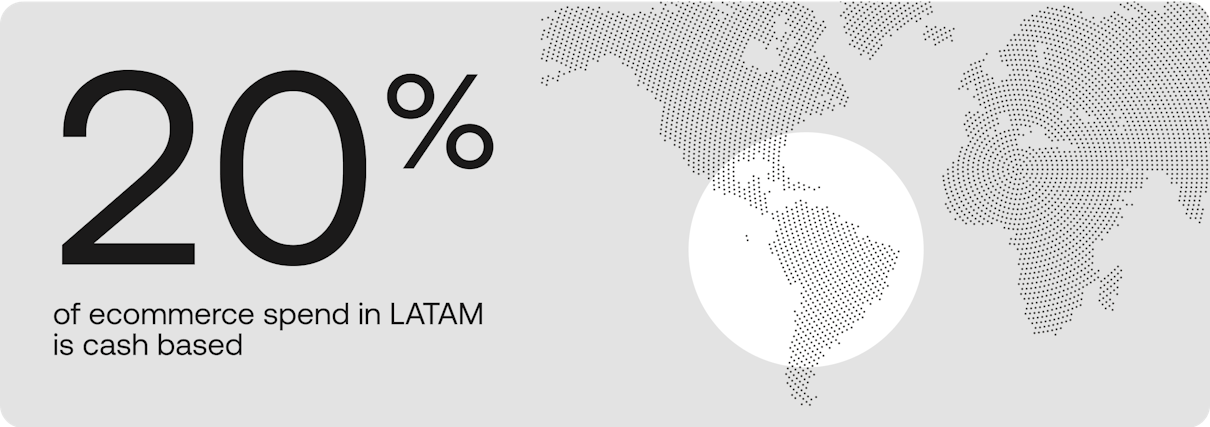
Cash-based payments are widely favored as a payment method in certain areas, notably Latin America, where they constitute 20% of ecommerce expenditure.
Cash-based payments typically commence with issuing a voucher containing a barcode given to the customer upon checkout. This voucher can be utilized at any participating physical store or bank, allowing the customer to pay using cash. Although integrating cash-based payments enables merchants to tap into a larger consumer base, they face challenges such as longer transaction confirmation times and extended settlement periods.
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency represents a digital payment solution that operates on blockchain technology, offering a decentralized and secure approach to conducting transactions. For example, TripleA's crypto payment gateway allows merchants to securely and effortlessly embrace cryptocurrency payments. Despite being a relatively recent development, cryptocurrency has become more popular as a payment method, especially in sectors such as gaming.

Digital wallets
Digital wallets have experienced rapid growth in popularity, particularly among unbanked populations where cash used to dominate. These wallets serve as electronic repositories of funds, enabling users to make payments conveniently using a unique identifier or their electronic devices. With no need for physical cards, consumers prefer digital wallets for their speed at checkout and secure transactions. The ease of use, security, and various top-up options have contributed to the swift adoption of this payment method.

Mobile wallets
Pass-through digital wallets such as Apple Pay and Google Pay function as virtual representations of financial accounts or cards, enabling users to make convenient contactless payments via cards or digital devices.
These pass-through digital wallets significantly enhance the checkout process by offering rapid biometric authorization and the ability to store additional information needed for checkout, such as the customer's address, phone number, and email. This streamlines the payment experience and improves overall transaction speed.

The growing trend of alternative payment methods around the world
In the 21st century, payment methods have undergone a remarkable transformation driven by evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements. As a result, alternative payment methods (APMs) have emerged, providing consumers with an unprecedented array of choices, ranging from the convenience of digital wallets to the flexibility of buy now, pay later options and the disruptive potential of Open Banking.
The growth in alternative payment methods is set to continue. In the European payments landscape, traditional cards' market share is expected to decline to 33% by 2026. In contrast, digital wallets, buy now, pay later, and bank-to-bank payments are projected to capture substantial market shares of 15%, 70%, and 10%, respectively.
The emergence of alternative payment methods is a global trend reshaping the digital economy. However, it's important to note that their development isn't uniform; it's fragmented and regional, shaped by a combination of politics, culture, and technology.
Let's take a quick tour around the world.
Alternative payment method development in Africa
APMs have become a driving force in the economic growth of sub-Saharan Africa, playing a significant role in shaping the region's financial landscape. International remittances to mobile-money wallets surged by 65% year over year, reaching around $1 billion. Digital wallets and improved interoperability between mobile wallets are gaining popularity, promoting financial inclusion across the continent.
One of Africa's most notable and transformative APMs is M-Pesa, which originated in Kenya and is used by 52 million individuals across the continent. M-Pesa operates through SMS-based technology, allowing users to conduct financial transactions effortlessly. Whether paying for goods, transferring money, or saving funds, M-Pesa has empowered millions of Africans with a convenient and accessible means of managing their financial lives.
Alternative payment method development in APAC
The Asia-Pacific (APAC) region is a prime example of a complex and highly fragmented market regarding payment preferences. This intricacy poses challenges for merchants seeking to cater to the payment needs of consumers across different countries.
Mobile payment methods dominate in China, where 92% of the population uses QR-code-driven e-wallets like Alipay and WeChat Pay.
PromptPay has emerged as one of Thailand's leading real-time proxy payment services. This system enables users to transfer funds instantly and securely, making it a popular choice for individuals and businesses. While in Indonesia, a preferred payment option is the OVO Wallet. This digital wallet platform has gained significant traction, providing users various services, including bill payments, online purchases, and peer-to-peer transfers.
Alternative payment method development in Europe
The European payments landscape is a diverse and intricate mosaic of various payment methods. While mainstream cards continue to dominate in key economies like the UK, there is also a strong preference for local payment schemes and online banking methods in different European countries. For example, Bancontact is at the forefront of electronic payments in Belgium. In the Netherlands, iDEAL is the leading online banking option. While Germany has embraced GiroPay as a popular bank transfer payment option.
Alternative payment method development in Latin America
Alternative payment methods account for 40% of Latin America's digital commerce payments. Pix in Brazil, PSE in Colombia, and digital wallets are notable APMs gaining momentum in the region. As APMs continue to evolve and gain acceptance in Latin America, their contribution to financial inclusion and the overall growth of the digital economy in the region is expected to be even more significant. Embracing and supporting alternative payment methods will be essential for businesses seeking to tap into the vast potential of this dynamic and expanding market.
Alternative payment method development in the Middle East
In recent years, the Middle East has emerged as a hotbed for payments innovation, witnessing a significant shift from its traditionally cash-centric approach to embracing digital payment methods. As e-commerce and mobile commerce have gained momentum in the region, various digital payment solutions, including mobile wallet payments like Apple Pay, have become commonplace among consumers. In addition to global payment solutions like Apple Pay, the Middle East boasts many popular local payment methods and schemes. For instance, Qatar's QPay and Kuwait's KNet have gained prominence. Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) is also witnessing regional growth.
Alternative payment method development in North America
The dominance of credit and debit card payments remains strong in this market, owing to their deep penetration and long-established presence. However, mobile wallets, such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, and PayPal, have been gaining popularity in North America, particularly as more commerce moves to mobile devices. Digital wallets account for approximately 32% of transactions in North America.
Among the emerging payment methods, Venmo is favored by the younger demographic, while ACH remains a prevalent choice for bill payments. Additionally, Buy Now, Pay Later brands like Afterpay and Paybright are rapidly expanding their market presence. Businesses operating in Canada should also be mindful of the domestic card scheme, Interac, which is used widely by individuals nationwide.
Benefits of alternative payment methods
From preventing cart abandonment to enhancing customer experience and expanding your customer base, offering alternative payment methods provides a range of benefits to merchants. Let's explore these in a little more detail.
Meeting local payment preferences
Businesses must localize their offerings when entering new markets. This includes payment methods, where businesses must understand and match local payment preferences. It can help instill trust and loyalty.
Faster transactions
A slow payment process will lead 76% of UK shoppers to abandon their carts. Alternative payment methods, like pass-through wallets such as Apple Pay and Google Pay on mobile devices, streamline the checkout process, enabling customers to complete transactions with just a few taps.
Additionally, concepts like Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) lower barriers to entry, making goods and services more affordable and accessible. As a result, these alternative payment solutions foster heightened satisfaction and increased customer loyalty.

Reduced risk of fraud
Robust security features like encryption and tokenization within alternative payment methods act as barriers against fraud. By adopting these measures, businesses can eliminate expensive chargebacks and unauthorized transactions, creating a secure payment ecosystem that strengthens customer trust and protects sensitive data.
Choosing alternative payment methods
Now we've explored the benefits of offering alternative payment methods and the diverse options in the market, the next question is how do you decide what payment methods to provide? Integrating a new payment method into your stack to reach more customers in the existing or new market will require carefully assessing the combination of factors. The popularity of an APM is not a guarantee of the perfect match for your business on the feature, UX, or technical level. Getting it right will help to manage risks better and increase conversion and customer retention while reducing costs.
Feature assessment
For different business types, certain APM features hold greater importance. Subscription-based services require secure recurring payment support and tokenization for managing involuntary churn. While wallets, bank transfers, and BNPL providers generally cater to this need, some regions may lack support for such payment flows.
In contrast, ecommerce players prioritize immediate payment confirmation and automated refunds to optimize processes and enhance customer engagement and loyalty. Bank transfers or wallet methods are preferred unless the region heavily relies on cash-based solutions. In such cases, payment lifecycle changes during offline payments must be carefully considered. Ecommerce businesses should also offer relevant BNPL options to increase buyer incentives and provide flexibility and convenience.
User experience
You clearly want to offer payment methods your customers want to use in your respective markets. But you also need to consider the experience the payment methods provide within your overall commerce flow. The payment touchpoint in your customer journey can either enhance the interaction with your product or create friction and uncertainty. Factors such as the authentication method and the number of redirections play a crucial role in shaping this experience. Be mindful of this experience when choosing which payment methods you offer.
Economic consideration
Carefully assess different payment methods by comparing fees, charges, security features, and integration complexity. Look for options that fit your financial means while offering strong security measures to protect your business and ycustomers'ers' sensitive information.
Integration and maintenance
It's common for the business to implement multiple APMs simultaneously on their roadmap. In this case, considering how the processors and all the APMs will be technically maintained and managed within your payment stack is as crucial as the implementation itself. Another option is using a solution like Primer, which provides seamless integration with multiple payment methods, enabling businesses to activate new options effortlessly.
The bottom line
Alternative payment methods have become increasingly crucial for businesses to maintain a competitive edge in the market. Providing customers with various payment options like digital wallets, mobile payments, and cryptocurrencies allows businesses to stay in tune with the shifting demands of their customer base. With Primer's unified payments infrastructure, you can streamline your payment process, create exceptional customer journeys, and conquer new markets.
Try Primer and ignite growth today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Are there payment methods I can use with no payment fees?
Payment methods involve multiple parties and processes, each with a unique fee structure.
Payment rails, which are mechanisms that allow the transfer of funds from one account to another, can be complex. Each party involved in the payment process, such as payment processors, banks, and card networks, may have their fee structures in place.
It is crucial to carefully review and compare the fee structures of different payment methods, considering factors such as transaction volume, currency conversion, chargebacks, and other potential costs.
Through diligent research and proactive negotiations with payment providers, businesses can find options that provide more favorable fee arrangements and greater transparency regarding the associated costs.
Which payment method is the best for paying globally?
Businesses should evaluate the regions or countries where they conduct business and identify their target markets for expansion. This understanding will help them tailor their payment methods to the preferences and behaviors of those specific markets.
They should also research the availability, acceptance, and practicality of various payment methods in their target markets, accounting for infrastructure and regulatory considerations to enhance cross-border transactions.